I recently had the opportunity to spend a week in São Paulo, Brazil, to meet with some infection control and infectious diseases folks. I came away feeling pretty disturbed and very grateful for the NHS.
I recently had the opportunity to spend a week in São Paulo, Brazil, to meet with some infection control and infectious diseases folks. I came away feeling pretty disturbed and very grateful for the NHS.
Brazil is a massive country, with almost 200m inhabitants. São Paulo is Brazil’s largest city, with more than 20m inhabitants making it the 7th largest city in the world. I have lived in London and close to New York, and spent quite some time in Tokyo but nothing comes close to the traffic in São Paulo. It took me 3 hours to travel the 30km from the airport to the hotel, not because it was the middle of the rush hour or because there was a problem, just because the volume of traffic is too big for the infrastructure to handle.
Brazil has around 7000 hospitals; 70% are private with a healthcare insurance system for those who can afford it. The public hospitals are the only option for those who cannot afford healthcare insurance. I visited a number of public and private hospitals and was struck by the following:
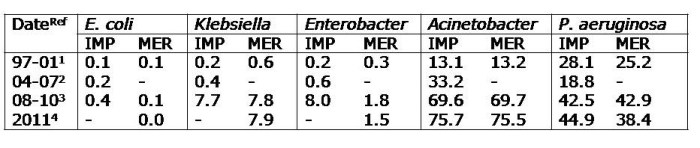
- Rates of antibiotic resistance are eye-wateringly high. Around 40% of healthcare-associated Klebsiella pneuomoniae are carbapenem-resistant and of these, around 20% are colistin-resistant. More than 50% of K. pneumoniae produce ESBLs. The situation with Acinetobacter baumannii is even worse, with >80% resistant to carbapenems. Whilst there is usually some treatment option left, pan-drug resistant Gram-negative bacteria are a daily reality on the ICUs. To top it off, around 60% of S. aureus are MRSA, 80% of E. faecium are VRE and C. difficile is chronically under-reported due to lack of testing infrastructure and limited awareness about sending specimens. There’s an excellent 2011 review on antibiotic resistance in Brazil here, although a lot has happened since 2011.
- The public hospitals are chronically overcrowded. This is best illustrated by a quick visit to the Emergency Department, where patients on stretchers line the corridors as far as the eye can see. These patients usually stay for days, not hours. The problem is so endemic that ICUs have been established in the ED. The wards are crowded too, with very small distances between beds. Plus, there are not enough staff to cover their beds, especially during nights and weekends. Following one meeting at a very large public hospital (2000 beds), we literally could not leave the building due to the sheer volume of patients trying to get in. Just like the roads, the volume of patients is too high for the infrastructure to handle.
- The contrast between public and private hospitals is stark. Instead of being met by patients on stretchers when you arrive at public hospitals, you’re met by glass fronted healthcare insurance offices.
So, what can be done? The various strategies to curb the growing threat of antibiotic resistance are as relevant in Brazil as elsewhere: prevention is better than cure; reduce antibiotic use; improve accurate and timely diagnosis; perform surveillance for action; embrace novel solutions; highlight the financial burden; and develop new antibiotics. Some progress has been made, for example, antibiotics are no longer available without prescription over-the-counter. The commitment and enthusiasm of the infection control and infectious diseases folks that I have met here is inspiring. However, they are limited by poor healthcare infrastructure, virtually no investment in microbiology laboratory facilities, lack of national reporting, the widespread availability of poor-quality antibiotics and extensive use of antibiotics in the veterinary sector, which makes progress difficult.
Next time you have the misfortune of visiting an Accident & Emergency Department in an NHS hospital, rather than moan if you have to wait a few hours to access world-leading healthcare free at the point of care, instead be thankful for the NHS.
Photo credit: Fred Inklaar.